Intro to MDSAP
What is MDSAP?
The Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP) is a single regulatory audit of a medical device manufacturer’s quality management system (QMS). The goal of the audit is to satisfy the requirements of multiple regulatory jurisdictions.
The FDA defines the MDSAP Program Policy as
“The single audit of a medical device manufacturer’s quality management system will include the assessment of design and development (where appropriate), Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs), adverse event reporting, and other applicable requirements of the participating regulatory authorities.”
MDSAP Audits address the challenges of increased product development costs, time-to-market, along with regulatory guidelines for testing and certification among different certifying boards.
Who needs to follow MDSAP requirements?
MDSAP is required for any Class II, III, or IV devices in Canada. MDSAP is not required for Class I in Canada. MDSAP is unnecessary for organizations that sell in the US and Europe unless your product sales extend to the other countries participating in MDSAP.
However, special considerations pertain to the US and Canada. In the US, MDSAP Audits can replace routine FDA inspections—unless there is a need for a “For Cause” audit. Canada is the only participant requiring medical device organizations to have MDSAP to sell in Canada.
How does MDSAP relate to ISO 13485?
ISO 13485 and MDSAP are different programs that overlap but are not identical. The MDSAP program is based on QMS requirements using ISO 13485.
ISO 13485 outlines specific requirements for a QMS that are based on a process approach. MDSAP has stricter rules and is an audit targeted toward the regulatory authorities in multiple countries.
What are the MDSAP participating countries and organizations?
MDSAP compliance means your organization has satisfied the requirements of MDSAP participant regulatory jurisdictions in the US, Australia, Brazil, Canada, and Japan.
The participating organizations include:
- Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration
- Brazilian National Health Surveillance Agency ANVISA
- Health Canada
- Japan Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency
- US Food and Drug Administration, Center for Devices and Radiological Health
There are also three participating affiliate members:
- Argentina’s National Administration of Drugs, Foods and Medical Devices (ANMAT)
- Republic of Korea’s Ministry of Food and Drug Safety
- Singapore’s Health Sciences Authority (HSA)
- Ministry of Health of Israel
What is the MDSAP assessment process?
All assessment activities follow a 3-year cycle. The cycle begins with an initial authorization, followed by two years of annual surveillance assessments. The medical device manufacturer undergoes a final recertification audit in the third year before their MDSAP certification expires.
For more general information on MDSAP, download the FDA’s FAQs Document.
Harmonize Requirements Through Global Consistency
The MDSAP Audit streamlines compliance efforts using regulations from all five participating countries.
The main challenge of MDSAP Audits is to consider all regulatory requirements in participating markets. To overcome this challenge, medical device manufacturers need to build consistent, predictable, simple, and transparent auditing processes.
Assess your current state and aim for:
- Ease of auditing
- Time-saving reporting
- Ability to track patterns and trends
The MDSAP Audit Approach (outlined below) and the expertise of external consultants build consistency in your quality and regulatory processes and harmonize the regulatory requirements you face.
The MDSAP Audit Approach
The MDSAP Audit approach started as an initiative at a 2012 international meeting in Singapore by the International Medical Device Regulators Forum.
The MDSAP Audit Approach is built on a foundation of risk management and comprises multiple processes and phases organized for efficiency. The processes combine the phases (outlined below) and incorporate tasks associated with device marketing authorization, facility registration, medical device adverse events, and advisory notice reporting.
The benefits of the MDSAP Audit Approach:
- Saves time, minimizes costs
- Reduces the burden of resource requirements
- Develops a successful framework for the design and implementation of a QMS
- Improves prioritization and allocation of resources
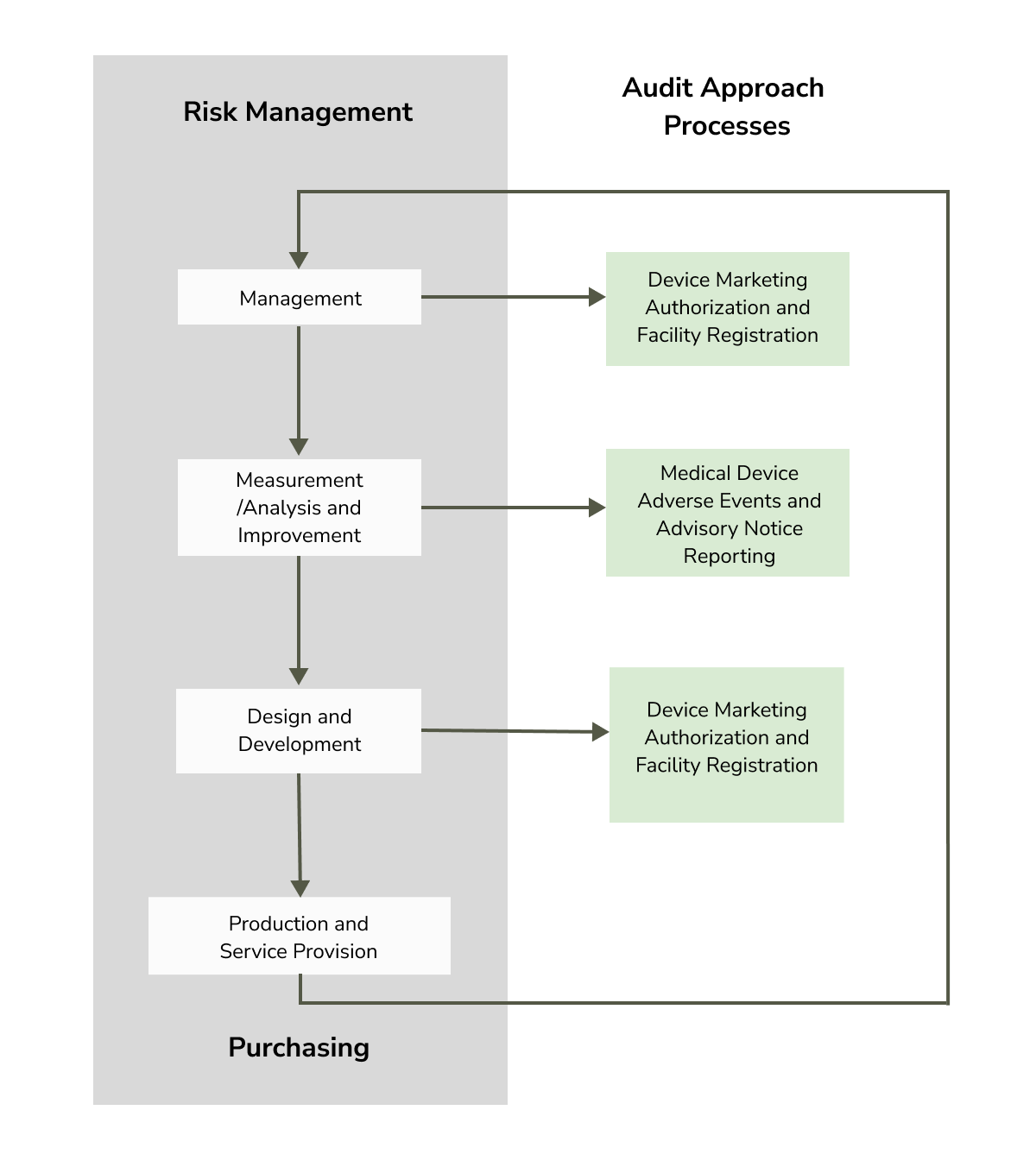
Illustration of MDSAP audit sequence and interrelationships from the FDA’s MDSAP Audit Process Report
Four Primary Phases of MDSAP Audit Approach
Phase 1: Management
The Management process is the first phase in the MDSAP Audit sequence. This phase ensures that the QMS is adequate, effective, and maintained. This means there are sufficient resources for everything from device design and manufacturing to quality assurance.
The management process ensures that the appropriate personnel has a defined QMS infrastructure.
The tasks include defining and executing:
- QMS planning, implementation, changes, and quality manual.
- Management representative responsibility and authority.
- Top management commitment to quality.
- Management reviews.
- Quality policy and quality objectives.
- Organizational structure.
- Extent of outsourcing.
- Personnel competency assessment and training.
- Risk management planning and review.
- QMS documentation.
- Distribution of devices with appropriate marketing authorization.
Phase 2: Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement
Phase 2 identifies any potential or existing problems with medical device quality.
The goals of this phase are to assimilate information, concentrate on product quality and design issues, and implement corrective or preventive measures for the future.
This phase focuses on quality data sources to investigate underlying causes of nonconformity. It is structured in a risk-based approach that ensures corrective measures and prevention implementation.
Medical device manufacturers should assess design or process changes needed for the redesign of the device and develop a plan of action for non-conforming products.
Finally, there is an internal audit to ensure compliance. This includes
- Information supplied for management review.
- Evaluation of information, including complaints.
- Communications with external parties about the complaints.
- Adverse event reporting.
- Advisory notices for evaluation of quality problems.
Phase 3: Design and Development
The final two phases begin with a design and development process. This process aims to show whether the medical device organization has defined and documented procedures that are implemented according to specific requirements.
The steps include:
- Technical documentation.
- Selection of a completed design and development project for review.
- Design and development planning.
This phase should demonstrate proper implementation of the design and development process. The audit phase shows the process has adequate review, validation, verification, design transfer, and design changes.
The design process must be complete, coherent, and unambiguous—with risk management activities in place to mitigate product risk.
The design should meet the requirements of the specific medical device application. Clinical evaluation should include medical device safety and performance as well as meet user needs for proper packaging and labeling.
If software is part of the design process, then the software should meet the same product specifications.
Phase 4: Production and Service Controls
The production and service controls process represents the final phase. It aims to ensure the product meets design specifications and requirements. This audit portion concludes any testing, infrastructure, facilities, equipment, and servicing for verification. Its primary objective is to confirm the medical device company will develop products according to its design and specifications.
A purchasing audit wraps up this phase and confirms the products and services comply with purchase requirements and specifications.
Outsourcing MDSAP Audit
The MDSAP offers the benefits of efficiency and compliance. However, preparing for MDSAP audits is time-consuming and complex. Outsourcing MDSAP tasks to experienced quality assurance and regulatory affairs consultants can help you streamline and customize the MDSAP audit approach.
QA Consulting offers a full range of services, including MDSAP audit preparation, training, education, and mock audits. We have the expertise and adaptability to assist your medical device organization in the MDSAP program.






